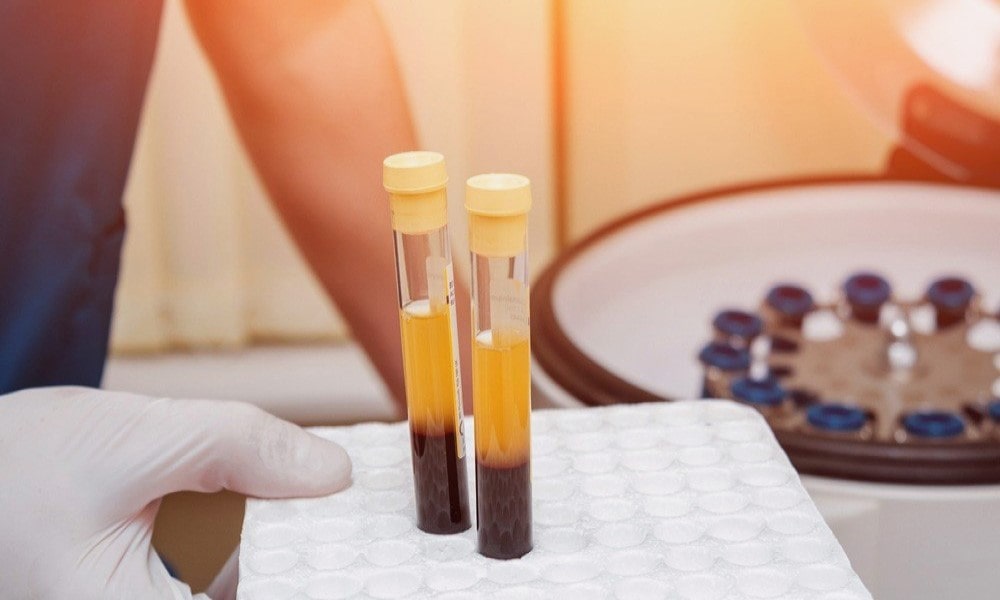
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a popular medical and cosmetic procedure with diverse applications. The key to its success is proper PRP preparation, typically using vacuum-sealed tubes capable of holding blood samples for platelet concentration.
Various PRP systems and kits may require different PRP tubes, which can hold separating gel, buffy coat layers, or sodium citrate solutions for effective PRP extraction. You may visit the website of Plasmolifting World at https://plasmolifting.shop/de/14-plasmolifting-prp-roehrchen to learn more about PRP tubes.
What are PRP tubes?
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) tubes are vital tools for medical professionals seeking to harness the therapeutic potential of autologous plasma. These tubes feature a thixotropic gel that effectively separates plasma from undesirable cellular components, yielding high-purity, therapeutically potent plasma.
PRP, with its regenerative properties, has been applied in various medical disciplines for over a decade, including:
- Dentistry
- Surgery (maxillofacial, cardiac, orthopaedic)
- Ophthalmology
- Urology
- Wound treatment.
The resulting autologous plasma is suitable for injection, offering promising clinical benefits across diverse medical fields.
The two tubes required for PRP preparation
PRP preparation involves isolating platelet concentrate from a blood sample through centrifugation. The choice of tools and accessories varies based on the treatment type, centrifuge used, and treatment goals. Typically, two types of tubing are employed in the process.
1. Vacuum-sealed blood centrifuge tubes
In conventional PRP preparation, blood is drawn from the patient and placed in a centrifuge. Vacuum-sealed blood centrifuge tubes are essential, with or without using PRP gel or anticoagulants like sodium citrate, to ensure the success of this process.
These tubes minimize the risk of contamination and facilitate easy platelet recovery. However, it is crucial to consider the need for anticoagulants if there is a delay between blood collection and centrifugation, as blood can quickly clot, resulting in platelet-poor plasma if not promptly processed.
Such considerations are vital to maintain the quality and efficacy of the resulting PRP treatment.
2. Blood collection tubes
Additional medical blood collection tubes become vital in specific procedures where the manual addition of compounds like sodium citrate is necessary before centrifugation. Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount, especially if blood is frequently transferred between tubes.
While a proper transfer needle can reduce the risk of contamination, tube sterility remains a concern.
Blood collection tubes also prove beneficial when conducting alternative platelet therapies, such as plasma-rich fibrin matrix treatments, where additional manipulation of the blood sample is required.
The specific type of tubes may vary based on the practitioner’s preference and available equipment, but adhering to the highest standards of cleanliness and sterility in PRP preparation is always essential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PRP therapy relies on meticulous preparation, utilizing specialized PRP tubes that facilitate the extraction of high-purity autologous plasma rich in therapeutic platelets.
These tubes, equipped with thixotropic gel, ensure adequate plasma separation from unwanted cellular components during centrifugation, preventing contamination.
PRP’s regenerative potential has found application in various medical fields, from dentistry to surgery, ophthalmology, urology, and wound treatment.
The two primary types of tubes involved—vacuum-sealed blood centrifuge tubes and medical blood collection tubes—play distinct roles in the preparation process, crucial for maintaining the quality and efficacy of PRP treatments across diverse medical disciplines.










Comments