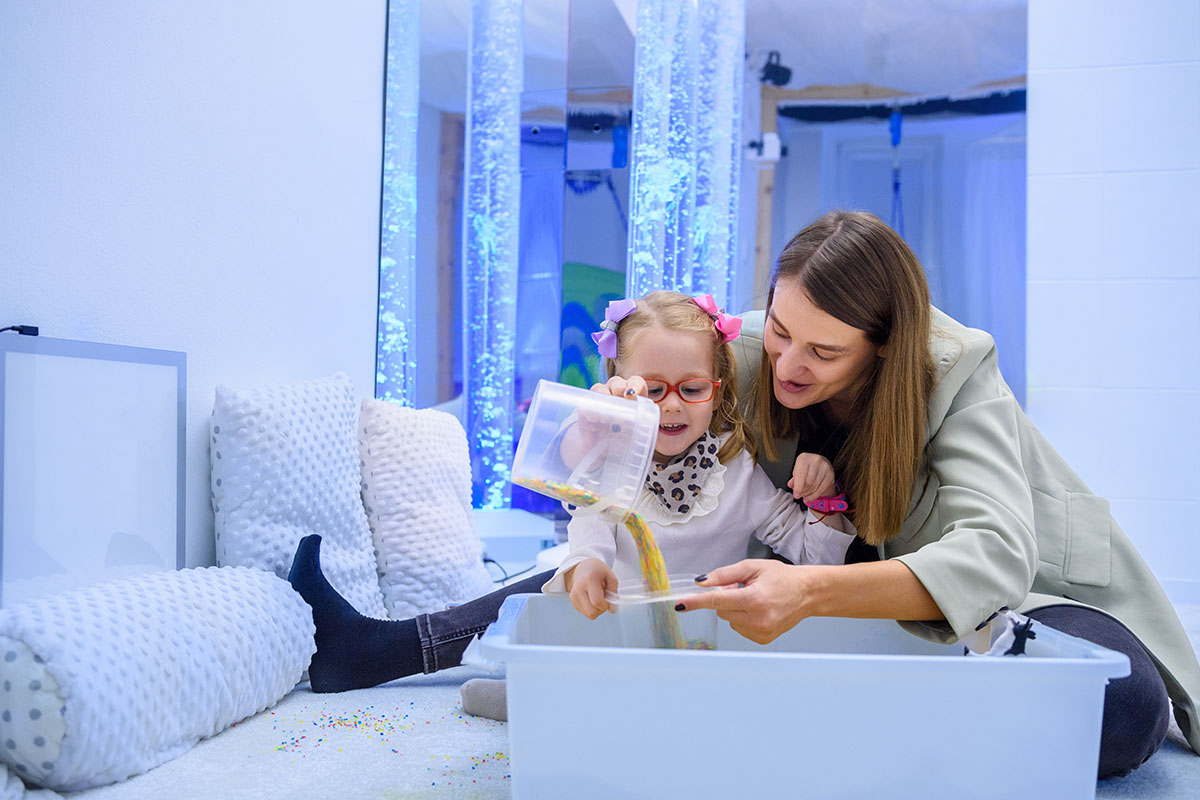
Life skills training is a critical component in the development of children with special needs, equipping them with the necessary tools to navigate the complexities of everyday life. By fostering independence through these skills, children are better prepared to face challenges and engage with their communities more effectively.
Defining Life Skills in the Context of Special Needs
Life skills encompass a broad range of competencies that enable individuals to manage personal and work-related tasks. For children with special needs, these skills are tailored to address their unique challenges and may include:
- Communication abilities
- Personal care routines
- Social etiquette
- Financial management basics
- Problem-solving strategies
The Impact of Life Skills on Independence
The acquisition of life skills has a profound impact on the independence of children with special needs. Mastery of these skills:
- Enhances self-confidence
- Promotes self-sufficiency
- Reduces reliance on support systems
- Facilitates integration into society
Assessing Individual Needs for Tailored Training
To ensure the effectiveness of life skills training, it is essential to assess each child’s individual needs. This process involves:
- Identifying strengths and areas for improvement
- Setting realistic and achievable goals
- Developing a personalized training plan
- Continuously evaluating progress and making necessary adjustments
By understanding and addressing the specific requirements of each child, life skills training can be optimized to foster greater independence and quality of life.
Designing Effective Life Skills Programs
Key Components of a Successful Program
A successful life skills program for children with special needs hinges on several key components. These include a curriculum tailored to the individual’s abilities, a focus on real-world applications, and the flexibility to adapt to each learner’s pace. Ensuring that the program is comprehensive and covers various aspects of daily living, such as personal care, communication, and social skills, is crucial for fostering independence.
Incorporating Evidence-Based Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of life skills training, it’s essential to incorporate evidence-based practices. This involves using strategies and interventions that have been scientifically proven to work. Such practices may include behavioral modeling, task analysis, and systematic instruction. These methods help ensure that the skills taught are retained and can be applied in various settings.
Collaboration with Parents and Caregivers
The role of parents and caregivers cannot be overstated when it comes to reinforcing life skills training. Collaboration with these key stakeholders ensures that the skills learned are practiced and reinforced at home. Strategies for this collaboration might include regular communication, training sessions for parents, and involving them in the goal-setting process. This partnership is vital for creating a consistent learning environment and for the child’s overall success.
Teaching Strategies for Diverse Learners
Adapting Methods to Suit Different Abilities
Educators and therapists often face the challenge of meeting the varied needs of children with special needs. To address this, they must adapt teaching methods to suit different abilities, ensuring that each child can engage with the material at their own level. Strategies may include:
- Simplifying instructions for better comprehension
- Using visual aids to reinforce concepts
- Providing hands-on activities to enhance engagement
Using Technology to Enhance Learning
The integration of technology in education has opened new avenues for children with special needs. Interactive apps, software, and assistive devices can make learning more accessible and enjoyable. Examples of technology use include:
- Speech-to-text programs for children with communication difficulties
- Educational games that adapt to a child’s learning pace
- Tablets with specialized applications for skill development
The Role of Repetition and Routine
Consistency is key when teaching life skills to children with special needs. Repetition and routine help to solidify learning and foster independence. Educators should incorporate these elements by:
- Repeating key concepts in various contexts
- Establishing a predictable schedule
- Using consistent cues and reinforcement techniques
By employing these strategies, educators can create a learning environment that acknowledges the unique challenges faced by children with special needs, while promoting their independence and growth.
Integrating Life Skills into Daily Routines
Incorporating life skills training into the daily routines of children with special needs is a critical step towards fostering independence. By embedding these skills into regular activities, children can practice and reinforce their learning in a natural context, leading to better generalization and retention.
Practical Approaches to Skill Generalization
Generalizing skills across various settings and situations is essential for children to apply what they’ve learned effectively. Educators and caregivers can:
- Identify common daily activities that can serve as learning opportunities.
- Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Use consistent cues and language to help children make connections between different contexts.
Creating Opportunities for Practice at Home and School
Practice is key to mastering life skills, and both home and school environments offer abundant opportunities. Strategies include:
- Collaborating with parents to ensure skills are reinforced at home.
- Setting up role-play scenarios that mimic real-life situations.
- Encouraging children to take on responsibilities, like classroom jobs or household chores, that utilize their skills.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Goals
Ongoing assessment of a child’s progress is vital to ensure that life skills training is effective. This involves:
- Keeping detailed records of skill acquisition and areas needing improvement.
- Being flexible and ready to adjust goals as children develop and their needs change.
- Celebrating successes, no matter how small, to build confidence and motivation.
Empowering Children Through Supportive Communities
Creating a supportive community is essential for empowering children with special needs. These communities provide a foundation for building self-confidence and fostering independence.
Building a Network of Support
A strong network of support can significantly enhance the quality of life for children with special needs. This network often includes:
- Family members
- Educators
- Healthcare professionals
- Peer groups
- Advocacy organizations
By connecting with these groups, children can access a variety of resources and experiences that contribute to their personal growth.
Encouraging Peer Interaction and Social Skills
Social interactions are a critical component of a child’s development. Encouraging children with special needs to engage with their peers can help them to:
- Develop communication skills
- Learn appropriate social behaviors
- Build friendships
- Gain a sense of belonging
These interactions can be facilitated through structured social groups, inclusive educational settings, and community events.
Promoting Advocacy and Self-Determination
Teaching children to advocate for themselves is a powerful step towards independence. It involves:
- Helping them understand their rights
- Encouraging them to express their needs and preferences
- Supporting them in decision-making processes
Fostering self-determination enables children to take control of their lives and to pursue their goals with confidence.











Comments