Gums serve as the supportive base around teeth, securing them in place. When bacteria and plaque accumulate, it can result in inflammation and harm to both teeth and gums, leading to gum recession, loss of attachment, and eventual tooth loss. However, pocket reduction surgery offered by the gum specialist in Dieppe, NB is an effective solution for improving gum health.
A comprehensive guide to pocket reduction surgery
Pocket reduction surgery, alternatively known as gingivectomy, osseous surgery, or flap surgery, is a surgical intervention designed to eliminate harmful bacteria lodged between the gums and teeth.
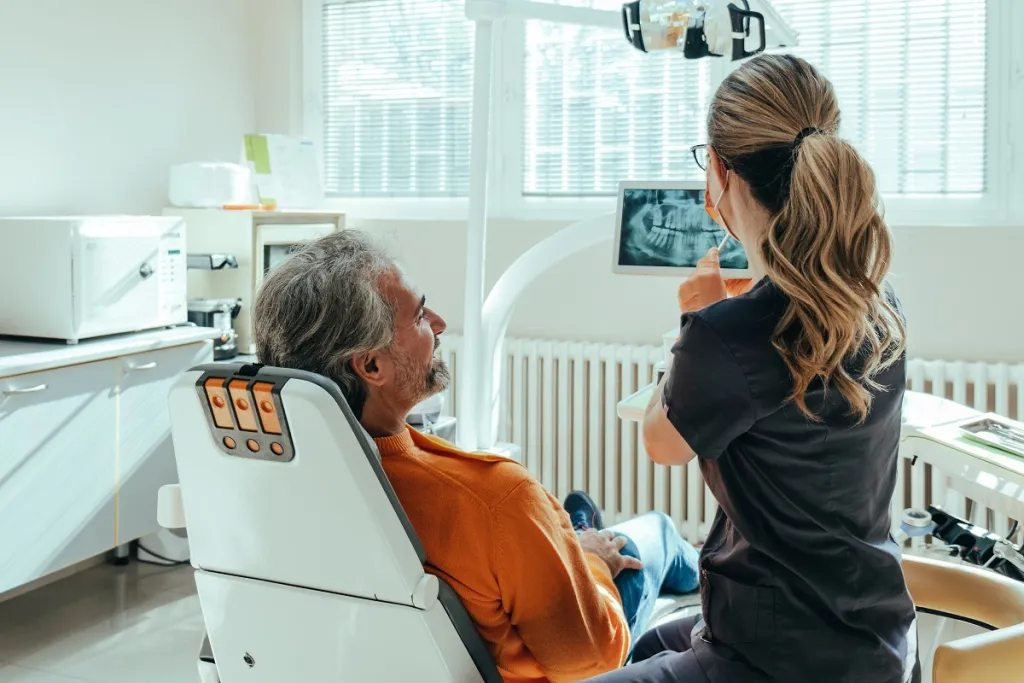
The oral microbiome comprises various strains of acid-producing bacteria that erode tooth structure and extend beyond the gum margin, compromising the alveolar bone. This process culminates in the development of gingival pockets, which deepen with disease progression. Consequently, gingivitis advances to periodontitis, ultimately resulting in tooth loss. Pocket reduction surgery intervenes in this damaging cycle by arresting its progression and reducing the depth of pockets harboring bacteria.
Pocket reduction surgery is a common procedure with the following goals:
Reduces bacterial spread
- Oral bacteria is believed to be a causative agent for several other health problems like diabetes, and heart disease.
- The surgery aims to eliminate bacteria and reduce the risk of secondary infections.
Halts bone loss
- This surgery removes bacteria from the gingival pockets and curbs the damage to the gums and alveolar bone, preventing tooth loss.
Improves the smile
- Periodontal disease causes changes in your oral cavity that are not attractive to the naked eye.
Aids in proper home care
- With the pocket reduction surgery, you can gain access to the subgingival area to maintain proper oral hygiene, through brushing and flossing.
How is pocket reduction surgery performed?
Your dentist will evaluate your oral cavity through visual examination and dental X-rays, to assess the condition of your teeth, gums, and jawbone.
- The surgery will be performed under local or general anesthesia (a numbing agent).
- A small incision (cut) will be made and the gums will be pulled back from the teeth, to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Your roots will be exposed to perform deep scaling. Root planing will be performed so that when the gums heal they will reattach to a smooth surface.
- Antimicrobial medication will be administered to remove any residual bacteria and promote healing.
- The gums will be sutured using small sutures and left in place for 5 to 7 days.
Progressive gum disease causing the formation of pockets can severely impact the underlying bone. Nevertheless, pocket reduction surgery not only prevents tooth loss but also enhances the aesthetics of your smile.








Comments