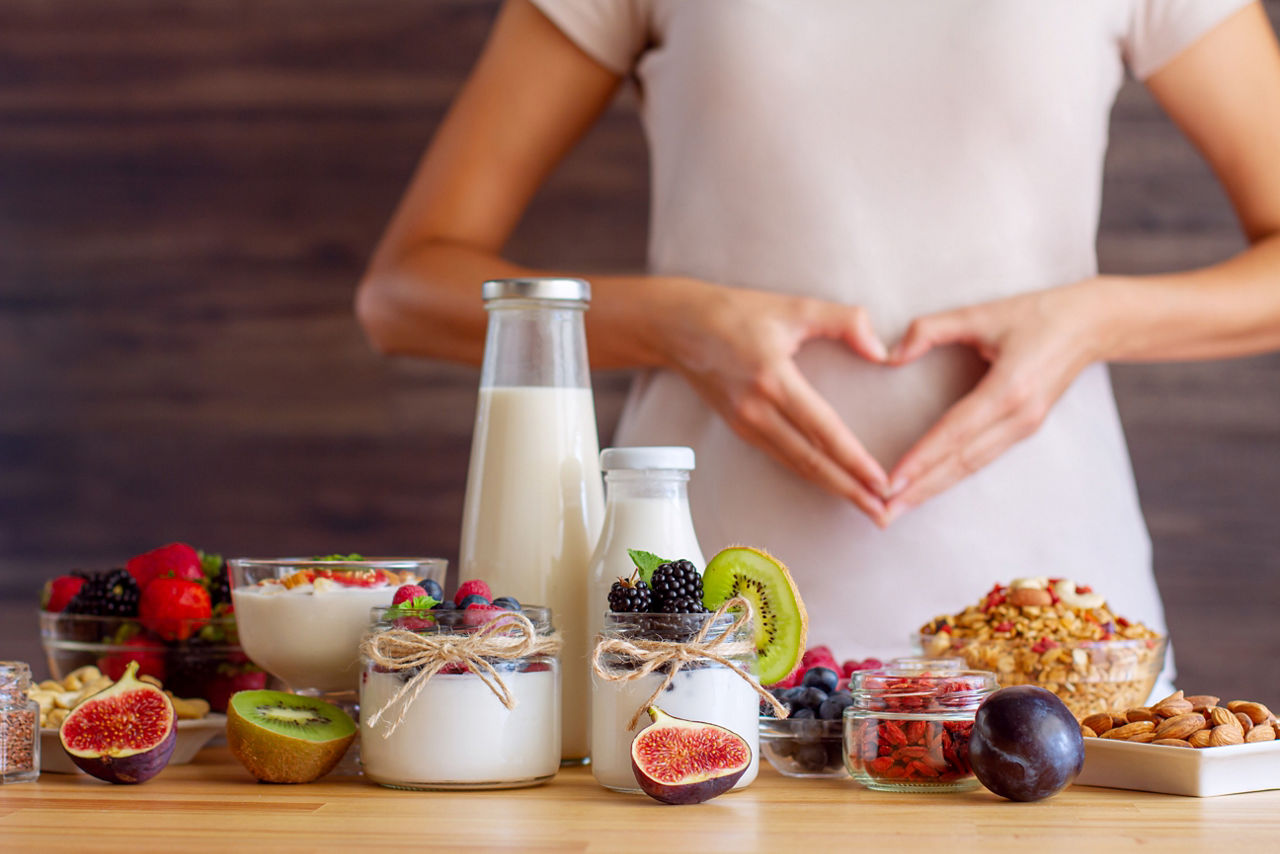

The human gut is a complex ecosystem teeming with trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. This intricate community of bacteria, fungi, and other microbes plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, influencing everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and mood regulation. To keep your gut microbiota in balance and promote optimal gut health, it’s essential to understand the roles of probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber in supporting a thriving gut environment.
About Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial bacteria help populate the gut microbiota, promoting a diverse and resilient microbial community. Probiotics have been linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and even mood regulation.
Sources of Probiotics
Fermented foods are excellent sources of probiotics. These include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, and kombucha. When choosing probiotic-rich foods, opt for varieties that contain live and active cultures and avoid overly processed options with added sugars and preservatives.
Taking Probiotic Supplements
In addition to fermented foods, probiotic supplements from brands like Supplement First are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. These supplements can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may have difficulty obtaining enough probiotics from their diet alone or for those looking to target specific health concerns.
About Prebiotics
Prebiotics are types of dietary fiber that serve as fuel for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Unlike probiotics, which are live microorganisms, prebiotics are non-digestible carbohydrates that pass through the digestive tract intact until they reach the colon, where they are fermented by gut bacteria.
Sources of Prebiotics
Many plant-based foods contain prebiotic fibers, including onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, bananas, chicory root, Jerusalem artichokes, and whole grains like oats and barley. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help nourish the beneficial bacteria in your gut and promote a healthy microbiota balance.
The Fiber Essentials
Dietary fiber is essential for gut health for several reasons. Firstly, fiber adds bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Secondly, certain types of fiber, such as soluble fiber, act as prebiotics, feeding beneficial gut bacteria and promoting their growth. Finally, fiber helps maintain a healthy gut environment by regulating inflammation and supporting overall digestive function.
Sources of Fiber
Fiber-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Aim to incorporate a variety of fiber sources into your diet to ensure you’re getting a diverse range of nutrients and promoting a healthy gut microbiota.
It’s a Balancing Act
Achieving optimal gut health is all about balance. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods, prebiotic fibers, and overall fiber essentials into your diet can help support a diverse and thriving gut microbiota. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep is crucial for promoting overall gut health and well-being.
Wrapping It Up
With a balanced approach to gut health, you can cultivate a resilient and flourishing gut microbiota that supports your overall well-being for years to come.










Comments