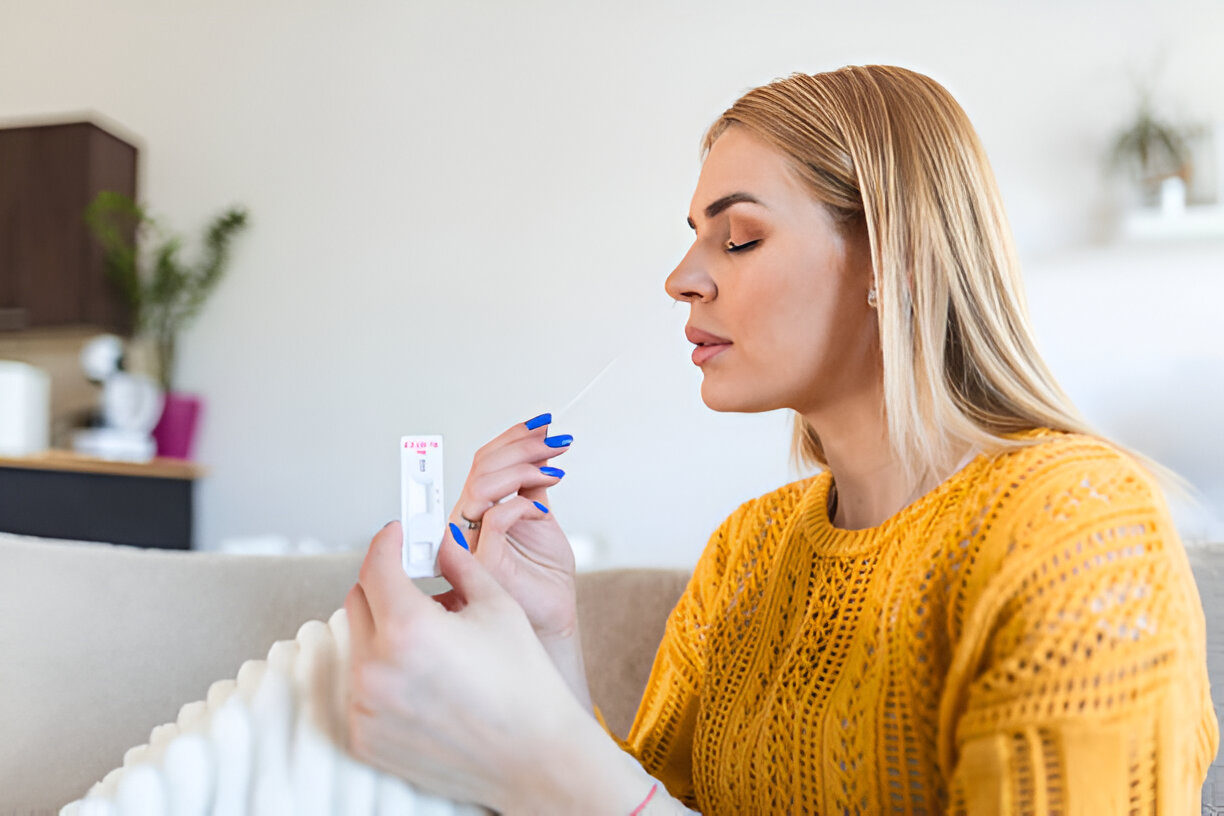
People depend on self-testing as one of the ways to monitor their health and halt the virus in the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Quick and easy ways of confirming that an individual has contracted coronavirus involve DIY solutions, especially with the use of home testing rapid antigen tests.
That brings us to a fairly phenomenal question: when should one apply these tests and how effective are they? Here is a closer look at why the self-assessment known as the OTC test can be a useful component of your COVID-19 management plan.
Convenience and Accessibility
Self-tests are intended to be simple to administer and yield findings quickly—typically in 15 to 30 minutes. Many American homes can order free tests through the government, and they can be purchased online and at pharmacies.
Ideal self-assessments are often not limited to any special equipment, or previous experience by the administrator of the tests and comes with directions. Having a chance to make a test at home, not going to the testing center or the doctor’s appointment is definitely an advantage for many.
How to Use a Self-Test?

When using a self-test, you always use a swab on your nasal area. When doing a test in a test tube containing the solution, you dip the swab in it and leave it to absorb some of the solution before putting a few drops of the solution on a test strip. You will examine the findings after setting a timer in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
It is good practice to precisely adhere to the instructions so as to obtain correct results. For instance, to avoid some kind of bias in the sample, you should not touch with the soft side of the swab. Also, remember that some tests may require different steps or extra stirring to mix the sample thoroughly.
Interpreting Results
In general, it is easy to interpret the findings of an at-home COVID-19 exam. The test is legitimate if a line appears in the control area. When there is no line in the test area, the result is negative, when there is a line in the test area, the result is positive.
Positive results can be indicated by even weak lines, therefore it is critical to pay attention to them. The test is deemed invalid, though, and you should try again using a different kit if there is no line visible in the control region.
Reliability of Self-Tests
These tests performed at home can be about 80% precise. Though this may seem like a great achievement, it entails that out of every five, one of the tests can produce wrong negative outcomes, particularly if one is yet to show symptoms. False negatives are dangerous because those people will be out circulating and potentially infecting others.
Even if you are currently feeling unwell or have had close contact with the infected individual, a negative result does not rule out COVID-19. In such circumstances, another test may be required or, and more accurate PCR test might be needed.
Conclusion
Self-tests provide a quick, convenient way to monitor COVID-19. While not perfect, they help detect potential infections and reduce virus spread. Combining testing with masks and social distancing ensures safety. Why not take control of your health with a self-test today?











Comments